#Computerized Maintenance Management System CMMS Software Applications
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
In today’s fast-paced industrial environment, ensuring the continuous operation and longevity of equipment is critical for success. One of the key pillars that supports this goal is maintenance management. It is a systematic approach to planning, scheduling, and overseeing all activities involved in the upkeep of assets, equipment, and facilities. Effective maintenance management not only reduces downtime and repair costs but also ensures the safety of workers and the consistent quality of products and services.
Maintenance management involves a range of tasks, from routine inspections and preventive maintenance to corrective actions and strategic planning. The primary objective is to keep equipment running at optimal performance with minimal unexpected breakdowns. Companies that implement well-structured maintenance strategies often experience increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and a higher return on investment.
There are several types of maintenance that fall under the umbrella of maintenance management. These include preventive maintenance, which involves regular and scheduled inspections or services to prevent equipment failure; predictive maintenance, which uses data and technology such as sensors and analytics to predict equipment failure before it occurs; and corrective maintenance, which addresses issues after a problem has already happened. A well-rounded maintenance management system incorporates all of these approaches to ensure balanced and effective asset care.
One of the most important tools in maintenance management today is Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS). These software applications help maintenance managers plan, track, and analyze maintenance activities. With a CMMS, businesses can monitor equipment performance, schedule routine inspections, track work orders, manage inventory of spare parts, and even evaluate maintenance costs. This data-driven approach increases efficiency, minimizes waste, and allows for better decision-making.
Another key aspect of maintenance management is workforce planning and training. Skilled maintenance personnel are essential to the success of any maintenance program. Employees must be trained not only in the technical aspects of their jobs but also in safety procedures and the use of maintenance software. Ongoing training and development ensure that the workforce remains competent and capable of handling evolving technologies and complex equipment.
Furthermore, the role of maintenance management is closely tied to safety and compliance. Equipment that is not properly maintained can pose significant safety risks to employees and the environment. Many industries, such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and aviation, are subject to strict regulations that require thorough documentation and regular inspections. Maintenance management ensures that these requirements are met, helping organizations avoid legal issues, fines, and reputational damage.
One of the major challenges faced in maintenance management is balancing cost with performance. While regular maintenance can prevent costly breakdowns, it also requires investment in time, labor, and resources. This is where strategic planning comes into play. Maintenance managers must analyze data, prioritize tasks based on risk and criticality, and allocate resources efficiently. By adopting a risk-based approach, companies can focus on the most vital assets and avoid over-maintenance of non-critical equipment.
In recent years, the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the field of maintenance management. Smart sensors and connected devices now allow for real-time monitoring of equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance at an unprecedented scale. These technologies not only reduce maintenance costs but also enhance overall operational efficiency by minimizing downtime and extending asset life.
In conclusion, maintenance management plays a vital role in the success of modern industries. It encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at ensuring the reliability, efficiency, and safety of equipment and facilities. By investing in advanced tools, skilled personnel, and strategic planning, organizations can build a proactive maintenance culture that drives productivity and long-term growth. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of effective maintenance management will only grow, making it a cornerstone of sustainable business operations.
0 notes
Text
What is Enterprise Asset Management?
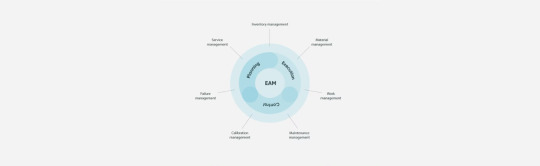
Enterprise Asset Management has a future in the cloud with SaaS services, as organizations are rapidly migrating to the cloud and services that are managed from a centralized location—ideal for asset management. Data needs can be more easily accommodated using cloud software, as there is flexibility in storage options and storage expansion.
An EAM system should be applied for better planning, execution, tracking, and optimization of assets and parts. EAM can sometimes be compared to computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), but there is a distinct difference between the two. EAM software and its holistic view can account for MRO parts and materials management, asset lifecycle management, service contracts, financial management, and analytics. EAM oversees assets and supports their performance from beginning to end, including a hierarchical asset database, inventory levels, utilization, and location as well associated documentation, work orders, and maintenance plans. CMMS are generally considered to be small-scale, single-site applications for work orders with less functionality overall.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
How to build a CMMS mobile app? Know about all features and costs by MAE
computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) is a software that helps organizations a lot in managing their support activities. The main motive behind this is that businesses should improve the maintenance of their resources, equipment and facilities so that their performance and progress can increase. The benefit of mobile CMMS apps, employees can access their maintenance tasks from anywhere.
Benefits of a Mobile CMMS App
Increased Productivity: Mobile CMMS apps empower maintenance teams to access important information and perform tasks easily. Technicians can quickly view work orders, access equipment manuals, and update maintenance records in real time.
Enhanced Data Accuracy: Mobile data entry helps technicians enter accurate and timely information into the system, reducing errors and verifying all integrity.
Reduced Downtime: Mobile CMMSapps help a lot in minimizing downtime as they provide prepared maintenance and quick response to equipment failure.
Key Features of a Successful Mobile CMMS App
Work Order Management:
Smoothly create, assign, and track work orders.
View details of work orders including priority, due dates, and assigned technicians.
Change work order status in real time.
Take and attach pictures and videos to work orders.
Inventory Management:
spare parts and consumables tracked.
purchase orders generated and tracking of inventory.
real time alerts for the low inventory level.
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling:
scheduling of avoiding maintenance work
receiving automated reminders regarding the upcoming activities of maintenance.
Asset Tracking:
Track the location and status of resources.
Report on resources utilization and performance.
Reporting and Analytics:
Report customized on maintenance costs, downtime, and KPIs.
Analyse data to determine trends and opportunities for improvement.
Integration Capabilities:
Integrate with other business systems, for example, ERP and CRM.
Offline Functionality:
Enable users to access and use the app even when offline.
User-Friendly Interface:
Make sure the app is user-friendly to navigate and operate, even to technicians with no technical background.
Building a Mobile CMMS App: The Process
1. Define Requirements and Scope:
Clearly define the specific needs and goals of your business.
Identify the primary features and functionality needed in the mobile application.
Identify the target audience and their specific needs.
2. Choose the Right Development Platform:
Select the right operating systems (iOS, Android, or both) according to your target audience and business needs.
Try cross-platform development frameworks like React Native or Flutter, which can minimize development time and costs.
3. Design the User Interface and User Experience:
Create a simple and smooth functionality that is easy to explore and use.
Focus on creating an effortless and engaging user experience.
Costs of Building a Mobile CMMS App
The cost of building mobile CMMS apps depends on various factors such as:
App Complexity: The more features, functionalities and integrations are added to an app, the more development time and cost increases.
Platform Choice: When you develop an app for both iOS and Android platforms, the cost of the app increases.
Development Team: The experience and knowledge of the development team can have a significant impact on the overall cost.
Partnering with best app development companies
It is very important to work with a reputable and experienced app development company especially when you are developing a mobile CMMS app.
Mobile App Experts is one of the top app development companies which is very famous in developing original and smooth mobile applications. This company offers you a wide range of developers, designers, and project managers who can help you to create custom CMMS apps for your personal needs.
Conclusion
Mobile apps are changing the way businesses manage and maintain their resources. By using mobile technology, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs and gain competitive advantage.
If you are thinking of developing a mobile CMMS apps for your business then it is a great thing, just keep in mind the benefits, features and development process given in this article. You can also get a successful app developed for yourself by associating with MAE and that too at the lowest price. Our team has developed CMMS apps for many companies which are growing at a very good level today.

#mobile app development#mobile application development#mobile app development company#ios app development#top app development companies#android app development#app developer companies
0 notes
Text
How to Create an Efficient Work Order System: A Detailed Guide
Are you searching for ways to optimize your work order management process? Struggling to manage all the maintenance tasks within your organization? A well-structured work order system can be the solution. Implementing an effective work order system is crucial for industries such as manufacturing, construction, and more. This guide will provide insights into creating a work order system tailored to your business needs.
What is a Work Order?
A work order is a formal document or request that authorizes and tracks specific tasks, services, or maintenance activities. It typically contains vital information such as job descriptions, locations, required materials, estimated labor hours, deadlines, and special instructions.
Work orders are essential tools in industries like construction, manufacturing, and facility management. They ensure that tasks are completed efficiently, accurately, and within the stipulated time, while also enhancing resource management and communication between teams.
Applications of Work Orders
Work orders are widely used across various industries to organize tasks and manage resources. Here are some common applications:
Manufacturing: Used to monitor production processes, allocate resources, and oversee product assembly.
Construction: Facilitates task assignments, material allocation, and progress tracking for specific jobs such as plumbing, electrical work, or carpentry.
Facility Management: Manages maintenance tasks, repairs, and upgrades, ensuring smooth operation of facilities.
IT Services: Tracks and manages tasks like software installation, troubleshooting, and system upgrades.
Automotive Repair: Outlines the services needed, parts required, and labor involved in vehicle repairs.
Landscaping: Organizes tasks related to garden design, installation, and maintenance.
HVAC Services: Manages the installation, maintenance, and repair of HVAC systems in buildings.
Cleaning Services: Assigns and tracks tasks for residential or commercial cleaning projects.
These examples highlight the flexibility of work orders, which can be adapted for various fields to ensure organized operations and efficient communication.
Types of Work Orders
Work orders can be categorized based on their purpose and the nature of the tasks. Common types include:
Preventive Maintenance Work Orders: Scheduled tasks to prevent equipment breakdowns and maintain optimal performance.
Corrective Maintenance Work Orders: Issued in response to identified malfunctions or issues.
Emergency Work Orders: Created for urgent, unexpected issues requiring immediate attention.
Project Work Orders: Used for complex projects involving multiple tasks and resources.
Inspection Work Orders: Scheduled for routine inspections to ensure safety, quality, or compliance.
Change Work Orders: Manage modifications or updates to existing processes or infrastructure.
Service Work Orders: Document customer service requests, detailing specific tasks and instructions.
Internal Work Orders: Coordinate internal organizational projects and tasks.
Organizations often combine these types to suit their operational needs.
Understanding Work Order Management
Work order management involves creating, organizing, tracking, and completing work orders. It ensures the effective allocation of resources and timely execution of tasks. Effective management improves productivity, minimizes downtime, and enhances operational efficiency.
Organizations can manage work orders manually using spreadsheets or adopt specialized software like Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) for greater efficiency and automation.
Steps to Create a Work Order
Here is a step-by-step guide to creating an effective work order:
Identify the Need: Determine whether a work order is necessary for a task or project, such as routine maintenance, equipment repair, or new installations.
Gather Information: Collect details like:
Job description
Task location
Required materials and resources
Estimated labor hours
Deadlines
Special instructions
Select a Template or System: Choose a standardized work order template or a digital management system to ensure consistency.
Fill in the Details: Input the collected information into the chosen format, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
Assign Resources: Allocate personnel, materials, and equipment based on requirements and availability.
Schedule the Work Order: Establish timelines, including start and completion dates, and set milestones if needed.
Communicate the Order: Share the work order with all relevant parties to ensure clarity on roles and expectations.
Monitor Progress: Regularly review progress, address issues, and make adjustments to keep the task on track.
Complete and Review: Verify that the work meets the specified requirements, assess the process for improvements, and update records before closing the order.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your work order process is both efficient and effective, contributing to the smooth operation of your organization.
0 notes
Text
Maintenance Repair & Operations (MRO) Procurement Intelligence 2024-2030: From Insights to Action
The maintenance repair & operations (MRO) category is expected to grow at a CAGR of 2.2% from 2024 to 2030. The increasing demand from the manufacturing industries, the high adoption of smart technologies, and the growing requirement to reduce equipment downtime are driving the category’s growth. Companies are increasingly using MRO services to manage their supply chain and inventory efficiently. It is mainly helpful when multiple materials are used in the production process and the absence of any particular material can have a significant impact on production. Robotics is one of the fastest-growing technologies in this category used for improving operational efficiency. It is widely implemented in the industrial, manufacturing, and aftermarket segments. The major applications include single-part repairs, carbon fiber manufacturing, and intricate inspection tasks using miniaturization, which enables robots to inspect components normally difficult for humans to access.
The category is fragmented with a mix of players ranging from spare parts suppliers to national and international-level distributors. MRO often involves a wide, fragmented network of suppliers providing anything from tools, safety equipment, and cleaning supplies. According to industry experts, there is a growth trajectory for aftermarket and maintenance, engineered and machined components suppliers in lower-tier (or, Tier 3) segments in fragmented markets. Companies are increasingly collaborating or collaborating with technology providers to improve their services or expand their product lines.
A few instances of recent developments include:
• In January 2024, Wurth’s division, “Wurth Electrical Wholesale Group” purchased a Poland-based company, TIM SA. The latter is one of the largest electrical materials distributors in Poland. The deal aims to expand and strengthen Wurth’s electrical wholesaling activities in Poland as TIM operates as the largest e-commerce platform in the nation, generating around 70% of revenue through online mediums. Post-purchase, both units under the acquiree-the wholesale and the logistics division-will continue to operate as independent companies.
• In September 2023, Applied Industrial Technologies (AIT) purchased two companies-Bearing Distributors and Cangro Industries. The acquisition will help AIT strengthen its local presence in South Carolina and New York and increase customer access. Both companies will benefit from expanded product lines as they get access to enhanced automation operations.
Order your copy of the Maintenance Repair & Operations (MRO) Procurement Intelligence Report, 2024 - 2030, published by Grand View Research, to get more details regarding day one, quick wins, portfolio analysis, key negotiation strategies of key suppliers, and low-cost/best-cost sourcing analysis
Labor, warehousing, rent and utilities, technology or IT infrastructure, and overheads. Other costs can include transportation, marketing, legal, or tax. Labor is the largest cost component. IT infrastructure is crucial as it includes elements like engineering systems, computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, and e-procurement systems that impact costs. A CMMS system allows firms to simplify maintenance operations by tracking equipment, inventory, and manpower. There are multiple pricing models in CMMS such as per-user per-month subscription model, tiered pricing models, and on-time perpetual licensing model. In 2024, CMMS software prices may range from as low as USD 30 per user per month to USD 350 per user per month for more complex capabilities. For a customized CMMS solution, the cost can range between USD 1,800 - USD 20,000. Mid-sized companies spend on average between USD 10,000 - USD 50,000 for a customized solution. Small companies can pay around USD 45 - USD 125 per month for a subscription-based model.
China is one of the most preferred countries for procuring industrial supplies and MRO services. While selecting the MRO service providers, clients should consider a number of factors, including product quality, service, and supplier reliability, years of experience and expertise in the target industry, shipping speed, and shipping costs. Other important considerations, under sourcing, include examining the seasonal patterns of MRO inventory demand and adjusting purchases accordingly.
Maintenance Repair & Operations (MRO) Sourcing Intelligence Highlights
• The maintenance repair & operations (MRO) category is fragmented. As a result of this fragmentation, the major challenges for vendors include high acquisition costs, poor visibility into demand, and duplication.
• The competitive rivalry is high among players due to low switching costs and industry fragmentation. One of the major barriers to entry among new entrants is information asymmetry as a result of information or data controls and manuals by manufacturers, OEMs, or vendors.
• Labor forms the largest component, accounting for a 40% - 50% share of the total cost structure.
• Some of the other preferred countries for procuring MRO services include Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey, and UAE (Dubai). These nations have consistently established themselves as reliable players in the APAC region. This is mainly due to the favorable government policies and tax incentives, the ability to create viable ecosystems, and the presence of cost-efficient skilled labor.
List of Key Suppliers
• Adolf Würth GmbH & Co. KG
• Air Liquide S.A.
• Applied Industrial Technologies, Inc.
• MSC Industrial Direct Co., Inc.
• Rubix Group International Limited
• Linde Engineering
• ERIKS Group
• Sonepar Group
• WESCO International, Inc.
• W. W. Grainger, Inc.
• RS Group (formerly Electrocomponents plc)
• Critica Infrastructure (Henkel)
Browse through Grand View Research’s collection of procurement intelligence studies:
• Meetings and Events Procurement Intelligence Report, 2024 - 2030 (Revenue Forecast, Supplier Ranking & Matrix, Emerging Technologies, Pricing Models, Cost Structure, Engagement & Operating Model, Competitive Landscape)
• Facilities Management Services Procurement Intelligence Report, 2023 - 2030 (Revenue Forecast, Supplier Ranking & Matrix, Emerging Technologies, Pricing Models, Cost Structure, Engagement & Operating Model, Competitive Landscape)
Maintenance Repair & Operations (MRO) Procurement Intelligence Report Scope
• Maintenance Repair & Operations (MRO) Category Growth Rate: CAGR of 2.2% from 2024 to 2030
• Pricing Growth Outlook: 8% - 15% (Annually)
• Pricing Models: Cost Plus pricing, contract-based pricing model
• Supplier Selection Scope: Cost and pricing, past engagements, productivity, geographical presence
• Supplier Selection Criteria: By types of services and supplies (industrial and production equipment, construction and infrastructure repairs, material handling equipment, tools and supplies, etc.), operational and functional capabilities, quality measures, standards followed, certifications, regulations, and others
• Report Coverage: Revenue forecast, supplier ranking, supplier matrix, emerging technology, pricing models, cost structure, competitive landscape, growth factors, trends, engagement, and operating model
Brief about Pipeline by Grand View Research:
A smart and effective supply chain is essential for growth in any organization. Pipeline division at Grand View Research provides detailed insights on every aspect of supply chain, which helps in efficient procurement decisions.
Our services include (not limited to):
• Market Intelligence involving – market size and forecast, growth factors, and driving trends
• Price and Cost Intelligence – pricing models adopted for the category, total cost of ownerships
• Supplier Intelligence – rich insight on supplier landscape, and identifies suppliers who are dominating, emerging, lounging, and specializing
• Sourcing / Procurement Intelligence – best practices followed in the industry, identifying standard KPIs and SLAs, peer analysis, negotiation strategies to be utilized with the suppliers, and best suited countries for sourcing to minimize supply chain disruptions
#Maintenance Repair & Operations (MRO) Procurement Intelligence#Maintenance Repair & Operations (MRO) Procurement#Procurement Intelligence 2024-2030
0 notes
Text
Digital Light Processing DLP Projector Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends [2032]
Digital Light Processing DLP Projector Market provides in-depth analysis of the market state of Digital Light Processing DLP Projector manufacturers, including best facts and figures, overview, definition, SWOT analysis, expert opinions, and the most current global developments. The research also calculates market size, price, revenue, cost structure, gross margin, sales, and market share, as well as forecasts and growth rates. The report assists in determining the revenue earned by the selling of this report and technology across different application areas.
Geographically, this report is segmented into several key regions, with sales, revenue, market share and growth Rate of Digital Light Processing DLP Projector in these regions till the forecast period
North America
Middle East and Africa
Asia-Pacific
South America
Europe
Key Attentions of Digital Light Processing DLP Projector Market Report:
The report offers a comprehensive and broad perspective on the global Digital Light Processing DLP Projector Market.
The market statistics represented in different Digital Light Processing DLP Projector segments offers complete industry picture.
Market growth drivers, challenges affecting the development of Digital Light Processing DLP Projector are analyzed in detail.
The report will help in the analysis of major competitive market scenario, market dynamics of Digital Light Processing DLP Projector.
Major stakeholders, key companies Digital Light Processing DLP Projector, investment feasibility and new market entrants study is offered.
Development scope of Digital Light Processing DLP Projector in each market segment is covered in this report. The macro and micro-economic factors affecting the Digital Light Processing DLP Projector Market
Advancement is elaborated in this report. The upstream and downstream components of Digital Light Processing DLP Projector and a comprehensive value chain are explained.
Browse More Details On This Report at @https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com/market-reports/digital-light-processing-dlp-projector-market-100556
Global Growth Insights
Web: https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com
Our Other Reports:
Global Early Phase Clinical Trial Outsourcings MarketMarket Share
Global Paraformaldehyde MarketMarket Growth
Spa Software MarketMarket
Desktop CNC Machines MarketMarket Share
Programmable DC Power Supplies MarketMarket Growth Rate
Dyes and Pigments MarketMarket Forecast
Global Data Labeling Solution And Services MarketMarket Size
Online Betting MarketMarket Growth
Auction House MarketMarket Analysis
Electronic Grade Hydrofluoric Acid MarketMarket Size
Global Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR) MarketMarket Share
Global Usb Portable Battery MarketMarket Growth
Indoor Location By Positioning Systems MarketMarket
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) MarketMarket Share
Exome Sequencing MarketMarket Growth Rate
Industrial Electric Vehicle MarketMarket Forecast
Global Basketball Equipment MarketMarket Size
Apps for Kids MarketMarket Growth
Connected Street Lights MarketMarket Analysis
Paste PVC Resin MarketMarket Size
Global Privacy Management Software MarketMarket Share
Global Herpes Treatment MarketMarket Growth
T-cell Therapy MarketMarket
General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) MarketMarket Share
Water Hardness Removal MarketMarket Growth Rate
Beta Cyfluthrin MarketMarket Forecast
Global Minimally Invasive Surgery Video Columns MarketMarket Size
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) Software MarketMarket Growth
Distributed Denial-Of-Service (DDoS) MarketMarket Analysis
Bio-Based 1,3-Butanediol MarketMarket Size
Global Civil Engineering Design Software MarketMarket Share
Global Glycerol Monooleate MarketMarket Growth
Travel and Expense Management Software MarketMarket
Ureteroscopy MarketMarket Share
Flexible Graphite Sheet MarketMarket Growth Rate
Blast Suppression Damper Market Market Forecast
Global FRP Prefab Bathroom MarketMarket Size
OLED Coater and Developer MarketMarket Growth
Plant based Hemostat Powder Market Market Analysis
0 notes
Text
AI in the Manufacturing Industry: Use Cases, Benefits & More

“Some people call this artificial intelligence, but the reality is this technology will enhance us. So instead of artificial intelligence, I think we’ll augment our intelligence.”
– Klaus Schwab
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has grown massively over the past decade. In fact, we are pretty sure that most of you would be familiar with “Alexa” or “Ok Google”, which are present in our everyday lives, in the form of home assistants.
Now, that was about your daily life and the usage of AI for every day. But if we say that AI has ventured into the manufacturing industry as well and it is booming? Would you believe us? After the AI in IT article, we are quite sure based on our facts, figures, and research that Artificial Intelligence in the manufacturing industry has opened doors to several possibilities.
So, in this article, let’s cover all of those aspects and how the manufacturing industry is changing ever since the involvement of automation in the industry.
The Role of AI in Manufacturing: Understanding the History & Modern-Day Solution
AI’s role began in manufacturing by the 1980s, where many businesses were searching for various ways to improve efficiency. Hence, AI came into the role where manufacturers used AI applications to capture and share worker knowledge. In short, rather than depending on clipboards, notes or word of mouth, the employees who worked in manufacturing factories codify knowledge into software systems. What are those software systems you ask? Well, those are computerized maintenance management systems, also known as CMMS, or manufacturing execution systems, that stands for MES. These two made the employees’ life easy. How? They made information-sharing convenient and faster while streamlining production through automation and providing real-time data collection and more.
If you ask about “the current scenario of AI in the manufacturing sector”, then we can say that in today’s world, AI is advanced and it hands down working for quality control, robotics, predictive maintenance and even safety hazard detection.
In fact, with the use of sensors to detect mechanical issues, like abnormal vibrations or temperature spikes, AI can alert the appropriate personnel about the problem and can also tell them How, When and with Which Tool, this problem can be fixed. See, modern day requires modern solutions, and this is just an example, we have a dedicated section of AI use cases in the manufacturing industry, that will talk about all the major use cases and how AI was helpful.
Did you know Modern-Day smart manufacturing solutions like L2L Dispatch, feature these along with many more AI-driven capabilities. That’s why the reports, according to MarketsandMarkets, are talking about how AI in manufacturing industry is expected to grow at a whopping $16.7 billion by 2026.
We say that the more shop floor workers have interactive sessions with AI-enabled technologies, it means the smarter these technologies will become and make their future better.
Major Use Cases of AI in Manufacturing Industry

1. The Rise of Cobots in Manufacturing Sector
Have you ever wondered who lifts all these heavy machinery in the manufacturing industry? It’s Cobots, short for Collaborative Robots who frequently work alongside humans and function as their extra hands. Cobots can learn many tasks. For instance, they can detect and avoid obstacles on the way. In fact, people who work in manufacturing often rely on cobots to do heavy lifting. For example, cobots in automotive factories are used to lift heavy car parts and hold them in place while human workers work on securing them. These cobots, ever since its development, have also been able to locate and retrieve items in large warehouses.
2. The Concept of Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing Sector
Manufacturing plants, railroads or other users of heavy machinery have started to use AI-based predictive maintenance (PdM) in servicing needs. If an equipment isn’t maintained properly and in a timely manner, then that firm would lose money and their precious time. Plus, if an organization does it quickly then also it’s a problem. Hence, PdM systems help to work on those issues by predicting what replacement parts will be needed and when. It also helps the workers because timely maintenance leads to better safety.
If you are wondering how PDM does all this, then it makes use of analytic capabilities of ML algorithms along with data from IoT sensors embedded in the equipment to monitor their conditions. Thus, helping workers and companies in finding out the issue before time.
3. The Use of AI in Supply Chain Management
We are sure that you must have come across the term supply chain management in manufacturing and would have noticed how big of a role it plays in the manufacturing sector. So, how does AI help in supply chain management? Typically, large manufacturers have supply chains with millions of orders, materials purchases, ingredients and what not. Handling these manually is energy draining and time consuming. To solve this, AI is used. But there’s more to AI in the supply chain.
For example, AI-powered demand forecasting accurately predicts trends and supply chain disruptions based on previous data collection. Also, when it comes to tracking shipments and on-time delivery of goods then AI helps by analyzing data and identifying patterns, helping managers make informed decisions.
4. AI is Excelling in Product Development
Another great example of artificial intelligence in the manufacturing industry is through development of newer products. AI helps to quickly glance through various data, wherein it acts like a benefit to help manufacturing industries decide what products to bring next in the market. AI also helps engineers to design new products, where they talk about what they want, and it creates several options where they can have a look at. This makes the design process faster and better.
How AI in Quality Assurance Is Impacting?
In the manufacturing sector, especially when it comes to electronics, paying close attention to every little detail is crucial. In the past, ensuring the quality of electronics and microprocessors was a manual task, carried out by skilled engineers who meticulously checked if everything was manufactured correctly and if all the circuits were properly set up.
But times have changed! Thanks to automation and AI, we now have image processing algorithms that can do this job automatically. Imagine installing cameras at strategic locations on the factory floor. These cameras can instantly and continuously assess whether each item being produced is flawless. With this smart technology, we can achieve real-time and efficient sorting of products. It’s like having a team of super-precise inspectors working tirelessly, ensuring that every single item meets the highest quality standards.
What are the Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing?

⦁ Improved Quality Control As you may know, AI is fast and when it comes to the manufacturing industry then AI can make the quality control faster. AI with its automation techniques can pick up microscopic errors and issues, improving productivity and defect detection by 90%.
⦁ 24/7 Support Artificial Intelligence in the manufacturing sector can work round the clock performing tasks with the same level of energy and accuracy. It doesn’t make mistakes or get injured, it works in any conditions and can operate a factory efficiently at any time.
⦁ Inventory/Warehouse Management AI helps with keeping track of things in warehouses. It goes through the historical data to check sales, stock inventory, trends and what not. This makes warehouses save money and have enough products. For instance, a clothing store can use AI to predict the things that people are interested in buying. It can check the past sales and weather forecasts to keep the right clothes. This helps them to store the exact amount of clothes.
⦁ Enhanced Productivity AI is good at simplifying complex calculations and coding and can-do tasks automatically, saving engineers precious time. With AI-driven automation, manufacturing employees can focus on creative aspects of their job, increasing productivity and unlocking the full potential. Along with that AI boosts productivity by providing easy access to insights, where engineers can quickly find suitable solutions for specific products.
What Are the Future Trends & Forecast About AI in Manufacturing?

Did you know Manufacturing sector is said to see great potential in the future? According to a survey by Deloitte, it is said that about 93% of firms are confirming that AI will play a pivotal role in technology to drive innovation and growth in manufacturing.
Here are some of the important statistics we have gathered to help you understand how big of an impact AI will have in the future. So, if you are interested, then let’s get into the actual facts.
Enhanced automation and robotics
Predictive maintenance and smart asset management
Advanced quality control and defect detection
Optimization of supply chain and logistics
Human-machine collaboration and augmentation
Enhanced data analytics and decision-making capabilities
Improved safety and risk management
Customized and personalized manufacturing processes
Adoption of digital twins and virtual simulations
Integration of AI with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies
Some of the mentioned future trends are still in use in the manufacturing industry, however, the technology will be more advanced and provide accurate results.
Final Note
Artificial Intelligence is playing a major role in various industries. In this blog, we talked about manufacturing and how AI is helping employees and industries to flourish and reach the highest horizons. From supply chain management to predictive maintenance, the integration of AI has brought a massive improvement in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
We’re curious to hear your thoughts on AI in the manufacturing sector. We know you must have your own ideas and research done. So, take a moment and share your perspective, tell us what you feel about the manufacturing industry and how AI is making an impact.
Manufacturing industry is booming and your insights matter, it can inspire many people. Engage in conversation with your friends or family and get to know their perspective? Together, let’s build an exciting future by learning and growing. For more such information on AI and related industries, you can follow our blog page and stay updated. Till then, we have informative blogs that you can scroll through and find out your best topic for discussion.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Efficiency: Future Trends in Mobile CMMS Software

In the dynamic landscape of maintenance management, the evolution of Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) has been pivotal in streamlining operations and enhancing productivity. Among the most transformative advancements within this realm is mobile CMMS software, poised to revolutionize the way maintenance tasks are executed and managed in the future.
Real-Time Data Accessibility: The future of mobile CMMS lies in its ability to provide real-time access to critical maintenance data. Gone are the days of relying solely on desktop systems or manual documentation. Mobile CMMS platforms empower maintenance teams to access work orders, equipment status, inventory levels, and other pertinent information instantly, irrespective of their location. This seamless flow of data ensures informed decision-making and swift action, ultimately minimizing downtime and maximizing asset performance.
Integration with IoT and AI: As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to permeate industrial landscapes, mobile CMMS will increasingly integrate with IoT-enabled devices and sensors. This convergence enables predictive maintenance capabilities, wherein equipment health is monitored in real-time, and potential issues are identified proactively. Moreover, the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms augments the predictive capabilities of mobile CMMS, facilitating predictive analytics for optimized maintenance schedules and resource allocation.
Augmented Reality (AR) for Remote Assistance: The future holds promising applications for Augmented Reality (AR) in mobile CMMS, particularly in remote assistance scenarios. Maintenance technicians equipped with AR-enabled devices can receive real-time guidance and visual overlays, aiding them in complex repair tasks or equipment inspections. This immersive technology not only expedites problem resolution but also serves as a powerful tool for knowledge transfer within maintenance teams.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: Mobile CMMS platforms are poised to become the central hub for collaboration and communication among maintenance stakeholders. Features such as in-app messaging, photo/video attachments, and collaborative task management streamline communication channels, fostering synergy between maintenance technicians, supervisors, and other relevant personnel. This enhanced collaboration ensures swift resolution of maintenance issues and promotes a culture of accountability and transparency within the organization.
Customization and Scalability: The future of mobile CMMS lies in its adaptability to diverse industry verticals and specific organizational needs. Customization options that cater to unique workflows, asset types, and regulatory requirements empower organizations to tailor their CMMS solution accordingly. Furthermore, scalability is imperative to accommodate the evolving needs of growing enterprises and expanding asset portfolios. Mobile CMMS platforms that offer modular architectures and flexible deployment options ensure scalability without compromising performance or usability.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Mobile CMMS solutions are poised to leverage the power of data analytics to drive informed decision-making processes. By harnessing historical maintenance data, performance metrics, and predictive insights, organizations can identify patterns, optimize asset lifecycle management, and allocate resources efficiently. Moreover, advanced reporting and visualization tools empower stakeholders to gain actionable insights into maintenance operations, facilitating continuous improvement initiatives and strategic planning.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: With the proliferation of mobile devices in the workplace, cybersecurity and data privacy emerge as paramount concerns for mobile CMMS adoption. Future-proof mobile CMMS platforms prioritize robust security measures, including data encryption, authentication protocols, and regular vulnerability assessments. Compliance with industry standards and regulations ensures the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive maintenance data, safeguarding against potential cyber threats and data breaches.
Enabling CMMS Software On-the-Go with Eagle CMMS
The future of mobile CMMS solutions is a tangible reality waiting to be embraced. It is characterized by innovation, efficiency, and empowerment, offering organizations the tools they need to excel in an ever-evolving digital landscape. By adopting mobile CMMS solutions that prioritize real-time data accessibility, IoT integration, AR-enabled remote assistance, enhanced collaboration, customization, data-driven decision-making, and stringent cybersecurity measures, businesses can unlock unprecedented levels of operational excellence.
Fortunately, Eagle CMMS stands at the forefront of this technological revolution, poised to exceed expectations and redefine asset management across various sectors. Our robust suite of tools empowers teams to optimize maintenance operations anytime, anywhere through seamless mobile applications. But we're more than just software; we're your dedicated ally in success. From tailored training to ongoing support and regular updates, our team is committed to ensuring that your system evolves in step with the latest industry standards.
So, why settle for mediocrity when you can soar with Eagle CMMS? Experience the difference today and elevate your asset management game to new heights! The time to harness the power of mobile CMMS is now, as it paves the way for a future where maintenance management is not just reactive but proactive, predictive, and ultimately transformative.
To learn more visit our website or sign up for a free 14-day trial.
0 notes
Text
South East Asia CMMS Market Report: Industry Insights & Future Trends (2023)
In the year 2023, the South East Asia Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) market achieved a remarkable valuation of US$ 101.9 million. This dynamic market is poised for substantial growth, with projections indicating it will surge to an estimated value of US$ 226.3 million by the year 2033. The expected growth represents a compelling Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.3% from 2023 to 2033.
Request a Sample of this Report : https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-17196
Key Takeaways
The South East Asia CMMS market is projected to grow at an impressive CAGR of 8.3% from 2023 to 2033, reaching a valuation of US$ 226.3 million by 2033.
Cloud-based CMMS systems are gaining prominence for their accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Mobile CMMS applications are becoming increasingly popular due to the proliferation of smartphones and tablets.
The market currently accounts for approximately 6% of the enterprise asset management market, underscoring its substantial growth potential.
The industrialization in South East Asia is driving the need for efficient maintenance processes, making CMMS software a crucial asset.
Challenges include integration within existing infrastructure and workforce training.
Customized solutions tailored to regional and industry-specific demands will be key to market success.
Drivers and Opportunities
The CMMS market in South East Asia is undergoing a transformative phase, driven by several key factors. One significant trend is the increasing adoption of cloud-based CMMS systems. These cloud solutions offer numerous advantages, including easy accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. This shift is attributed to the growing awareness among businesses about the benefits of digitalizing maintenance operations.
Another driving force behind this market’s growth is the proliferation of smartphones and tablets in South East Asia. Mobile CMMS applications are gaining traction, enabling maintenance personnel to access and update critical data from anywhere, enhancing operational efficiency and responsiveness. Furthermore, the CMMS market currently represents approximately 6% of the enterprise asset management market, reflecting its substantial potential for expansion.
Competitive Landscape – Regional Trends
South East Asia’s rapid industrialization over the past few decades has resulted in an upsurge of manufacturing plants, power facilities, and industrial complexes. These infrastructures require consistent maintenance and repairs to ensure optimal functionality. CMMS software emerges as a vital tool in streamlining and effectively managing these maintenance processes, positioning the market as an essential contributor to the region’s industrial growth.
Restraints
While the South East Asia CMMS market displays immense growth potential, it also faces certain challenges. These include the need for effective integration of CMMS systems within existing infrastructure and the requirement for training and upskilling the workforce to maximize the benefits of these systems. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial to unlocking the market’s full potential.
Region-wise Insights – Category-wise Insights
The South East Asia CMMS market is characterized by diverse regional dynamics and specific industry requirements. Different countries within the region may prioritize various categories of CMMS, ranging from manufacturing to energy. Tailoring solutions to meet these unique demands will be pivotal in capitalizing on market opportunities.
Request for Methodology: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/request-report-methodology/rep-gb-17196
South Asia CMMS Market Outlook by Category
By Solution:
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) Software
Cloud-based
Web-based
On-premise
Services
Consulting Services
Integration & Implementation Services
Support & Maintenance
By Enterprise Size:
Small Offices (1 to 9 employees)
Small Enterprises (10 to 99 employees)
Medium-sized Enterprise (100 to 499 employees)
Large Enterprises (500 to 999 employees)
Very Large Enterprises (1,000+ employees)
By Industry:
Finance
Banking
Insurance
Investment/Securities
Manufacturing & Resources
Discrete Manufacturing
Process Manufacturing
Resource Industries
Agriculture
Distribution Services
Retail
Wholesales
Transportation /Logistics Services
Warehousing & Storage
Shipping
Services
IT/Professional Services
Consumer & Personal Services
Media, Entertainment & Publishing
Travel & Hospitality
Legal Services
Public Sector
Government (State/Central)
Education
Healthcare
Aerospace & Defense
Non-profit
Infrastructure
Telecommunication
Energy & Utilities
Building & Construction
By Country:
Singapore
Malaysia
Thailand
Philippines
Vietnam
Indonesia
Rest of South East Asia
0 notes
Text
Beyond Efficiency: The Rise of Smart Solutions in Facility Management Software Market
In the ever-evolving landscape of facility management, where efficiency and sustainability are paramount, the integration of smart solutions has emerged as a game-changer. The Facility Management Software (FMS) market is witnessing a transformative shift as organizations seek more than just streamlined operations; they aspire for intelligent, data-driven decision-making processes. This article explores the burgeoning trend of smart solutions in the Facility Management Software market, unraveling the key players, opportunities, and challenges that define this dynamic sector.
Understanding the Facility Management Software Market
The Facility Management Software market has been a crucial asset for organizations looking to optimize their operations, manage resources effectively, and enhance overall productivity. Traditionally, FMS focused on basic functionalities such as maintenance scheduling, asset tracking, and space utilization. However, the contemporary landscape demands more sophisticated solutions that go beyond conventional efficiency.

Key Elements Driving the Shift to Smart Solutions
1. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration:
As the IoT ecosystem expands, integrating sensors and connected devices within facilities has become pivotal. This enables real-time monitoring of various parameters, such as energy consumption, equipment health, and occupancy levels. FMS with robust IoT integration allows facility managers to make informed decisions based on accurate, up-to-the-minute data.
2. Predictive Analytics:
Smart FMS leverages predictive analytics to foresee potential issues before they escalate. By analyzing historical data and patterns, these solutions can predict equipment failures, maintenance needs, and even forecast energy consumption. This proactive approach not only minimizes downtime but also contributes to significant cost savings.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML algorithms have empowered FMS to learn and adapt, providing insights that lead to more informed decision-making. These technologies enhance automation, enabling systems to self-optimize and adjust based on changing conditions. For instance, AI-driven scheduling can optimize workforce management and resource allocation.
The Major Players in the Smart FMS Landscape
IBM Tririga:
A leader in intelligent real estate and facility management solutions, IBM Tririga employs AI-driven insights to enhance space utilization, streamline lease accounting, and optimize maintenance processes.
ARCHIBUS:
Recognized for its comprehensive FMS suite, ARCHIBUS leverages IoT and mobile technologies to deliver real-time insights into space utilization, asset management, and environmental sustainability.
eMaint CMMS:
A cloud-based CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) solution, eMaint utilizes IoT and predictive analytics to revolutionize maintenance processes, ensuring equipment reliability and minimizing downtime.
Planon:
Focused on smart building technologies, Planon offers an integrated FMS platform with IoT integration for efficient space management, maintenance, and workplace services.
Nuvolo:
Positioned as a leader in Connected Workplace solutions, Nuvolo combines IoT, AI, and ML to deliver a unified platform for facilities, space, and service management.

Opportunities in the Smart FMS Market
1. Sustainability Integration:
Smart FMS plays a pivotal role in achieving sustainability goals. The integration of energy-efficient technologies, waste reduction strategies, and green building practices within these systems aligns with the growing emphasis on environmentally conscious facility management.
2. Enhanced User Experience:
The rise of smart solutions translates to improved user experiences. Mobile applications, intuitive dashboards, and AI-driven chatbots empower users to interact seamlessly with FMS, fostering greater engagement and collaboration.
3. Customization and Scalability:
Organizations are increasingly seeking FMS solutions that are not only tailored to their specific needs but are also scalable as their requirements evolve. The ability to customize and scale smart FMS platforms positions them as long-term strategic assets.
Challenges in the Smart FMS Market
1. Initial Implementation Costs:
While the long-term benefits are substantial, the initial costs associated with implementing smart FMS can be a barrier for some organizations. Convincing stakeholders of the return on investment and long-term savings is a crucial aspect.
2. Data Security Concerns:
The influx of connected devices and the extensive data generated raise concerns about data security. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information becomes imperative in the smart FMS landscape.
3. Integration Complexity:
Integrating smart FMS with existing legacy systems can be complex. Organizations may face challenges in ensuring seamless connectivity and data flow between disparate systems.
The Future Outlook
The Facility Management Software market is poised for continued growth, driven by the relentless pursuit of operational excellence and sustainability. The integration of smart solutions, fueled by IoT, AI, and predictive analytics, is reshaping the landscape. As the market evolves, a holistic approach that addresses challenges while leveraging emerging opportunities will be key to unlocking the full potential of smart FMS. The journey toward smart facilities is not just about efficiency; it's a strategic leap toward building resilient, sustainable, and intelligent spaces that adapt to the needs of the future.
#Soft Services Facilities Management Market#Hard Services Facilities Management Market#Facility Management Software Market#integrated facilities management market
0 notes
Text
Sail to Success: Unleash the Power of Maritime Software
As a Director of Sales at Chetu, a leading custom software solutions provider, I have witnessed firsthand the digital transformation sweeping across the shipping industry. With over 20 years of experience in software development and sales, including extensive work with maritime companies, I am passionate about harnessing technology to empower organizations and professionals. In this article, I aim to highlight how maritime software can chart a course toward greater efficiency, profitability, and resilience for businesses across the shipping sector.
The Digital Transformation of Shipping
The emergence of maritime software has coincided with the Fourth Industrial Revolution, as shipping companies increasingly embrace digitization. Technology is radically optimizing operations across the board, from AI-enabled analytics to IoT-connected vessels. Customer expectations have shifted towards real-time tracking, transparency, and personalized interactions, compelling businesses to prioritize digital innovation. Industry leaders are rising to the occasion; early adopters of maritime software have improved productivity by nearly 20% while reducing costs by up to 11%. As we sail into the future, it is clear that technology will be the driving wind in the sails of shipping success.
The Multifaceted Impact of Maritime Software
The diverse applications of maritime software are creating multifaceted impacts for shipping companies. In fleet management, computerized maintenance systems (CMMS) leverage data to enhance asset visibility and scheduling. Such tools can minimize equipment downtime by over 35% and maintenance costs by 8-12%. Logistics software provides shipment tracking and optimized routing to improve turnaround times and customer service. Navigation tools allow dynamic course-plotting based on weather, currents, and other variables for safer, more efficient voyages. The outcomes are wide-ranging, from bolstered security compliance to streamlined cargo operations. Organizations can sail smoothly toward savings, sustainability, and scalability with the right solutions.
Navigating the Challenges with Technology
While maritime software unlocks tremendous potential, I acknowledge its adoption can face challenges. Integrating new systems with legacy infrastructure can get complex for shipping companies. Another common barrier is change management; upskilled employees on software usage requires planning and investment. As a sales director who interacts closely with clients, I emphasize the need for phased implementation and training to ensure smooth sailing. My team also provides tailored solutions that align with the organization's strengths, limitations, and strategic priorities. With the right approach, these technologies can be leveraged seamlessly to drive progress. As expert navigators work with the winds and tides, technology partners must understand their clients' directions to keep them on course.
Leveraging Maritime Software for Competitive Edge
Given today's complex business environment, maritime software has become indispensable for a competitive edge. Data-driven insights from analytics tools allow companies to identify opportunities and risks and optimize decision-making. For instance, using predictive maintenance software, managers can take proactive actions to avoid delays and downtime. Those who need to catch up in adoption risk losing ground as rivals become more agile and productive. Maritime software has enabled innovation at leading companies like Maersk and given them a differentiated market position. Clients I have worked with have leveraged solutions from Chetu to unlock 20-30% faster time to market for new offerings. The key is viewing software not as a cost but as an investment into resilience and strategic growth.
Key Considerations When Choosing Maritime Software
When advising clients on software selection, I highlight the importance of aligning solutions with long-term business goals. Scalability enables adapting to evolving needs and workflows. Extensibility allows adding capabilities as required. Prioritizing user experience promotes adoption across teams. For global enterprises, multilingual interfaces and versatility across locations are critical. Above all, solutions must integrate securely with existing infrastructure to avoid disruptions. Migrating data or replacing entire systems can get complex otherwise. I also recommend partnering with software providers that offer customization for specific requirements. Our team's hands-on approach has helped clients maximize their return on investment in new technology. With long voyages ahead, choosing the right software is key to setting the course for enduring success.
Empowering IT Professionals and Tech Companies
As maritime software continues advancing, it presents tremendous opportunities for IT professionals and technology companies to make an impact. I advise keeping abreast of emerging technologies and best practices. Attend industry events, read IT publications, and connect with peers to exchange knowledge. Bring fresh ideas to the table on how technology can be applied innovatively. Proactively seek collaborations between your technical experts and operations teams within organizations to harness complementary strengths. For third-party partners like Chetu, contribute your experience to deliver solutions tailored for nuanced maritime needs. Develop talent and skillsets aligned with the digitalization of shipping. Ultimately, your goal should be adding value as a trusted navigator for your clients' needs.
Realizing ROI and Long-Term Benefits
While adopting new technology requires an upfront investment, maritime software generates significant short- and long-term ROI. Optimized workflows and accelerated operations have allowed companies to improve productivity by over 15% within a year of implementation. Enhanced data visibility reduces waste and asset losses, providing over 30% return in the initial phases. The long-term gains are even more substantial. With routines automated by software, teams can focus on higher-value work. Data-driven forecasting and planning enable smarter resource allocation. Overall, digitally transformed organizations are over 40% more likely to report revenue growth and high profitability. Integrating the right solutions helps businesses sail faster by harnessing the power of technological innovations.
Building Resilience and Adaptability
Technology plays a key role in building resilience to changing tides in the dynamic shipping industry. The software provides the agility to respond swiftly to new customer demands or compliance needs. For example, mobile apps allow freight companies to provide real-time tracking and updates. Analytics software enables scenario planning and contingency strategies in the face of various risks. The pandemic proved to be an accelerated learning experience, as companies with advanced systems adapted seamlessly to disruptions. Beyond stability, technology allows organizations to leverage uncertainties as growth opportunities. Like expert sailors navigating turbulent seas by tacking, maritime software provides data-backed insights to steer through challenges.
Embracing a Software-Centric Future
As maritime software continues making inroads into shipping, the future promises even smarter vessels, intelligent navigation systems, and increased automation. Emerging technologies like blockchain, robotics, and autonomous ships will reshape workflows. While these advances may seem disruptive, they provide more possibilities than perils for progressive companies. We must embrace software not as an option but as the definitive edge needed to stay competitive. Fortunately, each leap ahead enables us to gear up for the next one - with better data, stronger capabilities, and a forward-thinking mindset. Just as sailors watch the skies and prepare for coming weather, organizations must keep sight of the horizon and chart their course led by technology.
The winds of change are here to stay in the maritime industry. By harnessing the power of maritime software development, IT professionals and tech companies can play a pivotal role in enabling organizations to reach new heights of efficiency, resilience, and connectivity. As we set our sails into an increasingly digital future, our skills, insights, and solutions will be the guiding stars that lead the way toward enduring success. Comments
1 note
·
View note
Text
This article delves into the differences between Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) and Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) software. By exploring their respective functionalities, features, and applications, the reader gains a clear understanding of how these two types of software serve distinct purposes in managing maintenance and assets within an organization. The article aims to decode the unique characteristics of CMMS and EAM, helping businesses make informed decisions in choosing the right solution to optimize their maintenance and asset management processes.
#cmms#cmms software#maintenance management#maintenance software#predictive maintenance#preventive maintenance#facility management software
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) Market: Driving Efficient Maintenance Operations
Introduction:
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, organizations across various industries heavily rely on efficient maintenance practices to ensure optimal performance, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of their assets. To streamline and enhance maintenance operations, Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) have emerged as indispensable tools. CMMS solutions integrate cutting-edge software and data analytics to automate maintenance workflows, facilitate asset management, and improve overall operational efficiency. This article explores the dynamic landscape of the CMMS market, highlighting its key drivers, benefits, and future prospects.
The Growing Need for CMMS:
The global market for CMMS has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by several factors. Firstly, industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, energy, transportation, and facilities management face mounting pressure to maximize asset uptime and reduce maintenance costs. CMMS platforms provide real-time visibility into equipment performance, schedule preventive maintenance, and optimize inventory management, leading to improved asset reliability and reduced operational expenses.
Furthermore, stringent compliance regulations and the need for asset lifecycle management have propelled the demand for CMMS solutions. CMMS software helps organizations maintain accurate maintenance records, track regulatory requirements, and ensure compliance, enhancing safety standards and regulatory adherence.
Key Benefits of CMMS:
1. Enhanced Maintenance Planning and Scheduling: CMMS software enables organizations to plan and schedule maintenance activities efficiently. By automating work order generation, assigning tasks, and tracking progress, maintenance teams can optimize their workflow, prioritize critical tasks, and allocate resources effectively.
2. Improved Asset Performance and Reliability: CMMS solutions monitor asset health, capture real-time data, and generate performance reports. By leveraging predictive analytics and condition monitoring, organizations can proactively identify potential issues, schedule preventive maintenance, and minimize unplanned downtime.
3. Efficient Inventory Management: CMMS platforms streamline inventory management by providing accurate asset information, tracking spare parts usage, and automating reordering processes. This ensures that the right parts are available when needed, reducing inventory holding costs and minimizing equipment downtime.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: CMMS software assists organizations in meeting regulatory requirements by maintaining comprehensive records, tracking inspections, and automating compliance reporting. This promotes a culture of safety, reduces risks, and avoids penalties associated with non-compliance.
Market Trends and Future Prospects:
The CMMS market continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and changing customer requirements. Some key trends shaping the market include:
1. Integration of IoT and AI: CMMS platforms are increasingly incorporating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms to enable predictive maintenance capabilities. Real-time data collection, combined with AI-powered analytics, allows organizations to predict failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and extend asset lifecycles.
2. Cloud-Based Deployment: Cloud-based CMMS solutions are gaining traction due to their flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud deployment offers anytime, anywhere access to maintenance data, seamless software updates, and enhanced data security.
3. Mobile and Remote Accessibility: Mobile CMMS applications empower maintenance technicians to access work orders, update task status, and record maintenance data on the go. This mobility enhances efficiency, reduces paperwork, and accelerates response times.
4. Integration with Enterprise Systems: CMMS platforms are increasingly integrating with enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and other business systems. This integration enhances data sharing, facilitates seamless workflows, and provides comprehensive insights across the organization.
Conclusion:
As organizations increasingly recognize the importance of efficient maintenance operations, the demand for CMMS solutions is expected to surge. By leveraging advanced technologies, such as IoT, AI, and cloud computing, CMMS platforms offer unparalleled benefits, including enhanced maintenance planning, improved asset reliability, efficient inventory management, and regulatory compliance. The CMMS market is poised for further growth as industries seek to optimize maintenance practices, reduce costs, and maximize asset performance in an increasingly competitive business landscape.
0 notes